Crypto markets have experienced highly volatile months, even by crypto’s standards. The year began with rising inflation shortly followed by the Russian and Ukraine war, causing Bitcoin’s price to retrace significantly from the $50k level at which it stood by the end of 2021. This recent series of events have impacted the mining industry in a negative way.
The industry has grown tremendously boosting competition and elevating hash rate to sustained levels not seen before. These low prices has affected the mining industry profitability and as a consequence miner reserves have decreased, likely to cover companies day to day costs. Furthermore, we will explore China’s crackdown on mining long term effects by analyzing the current Hash Rate Distribution.
Quick refresher — the hash rate is the aggregate power contributed by miners to secure a proof of work blockchain. This computing power is used to solve cryptographic algorithms (SHA-256 in Bitcoin’s case) to process transactions and reach consensus in proof of work blockchains. This indicator serves to measure how strong a network’s security is, since the greater the hash rate the more difficult it becomes for an attacker to try to overtake 51% of the mining control.
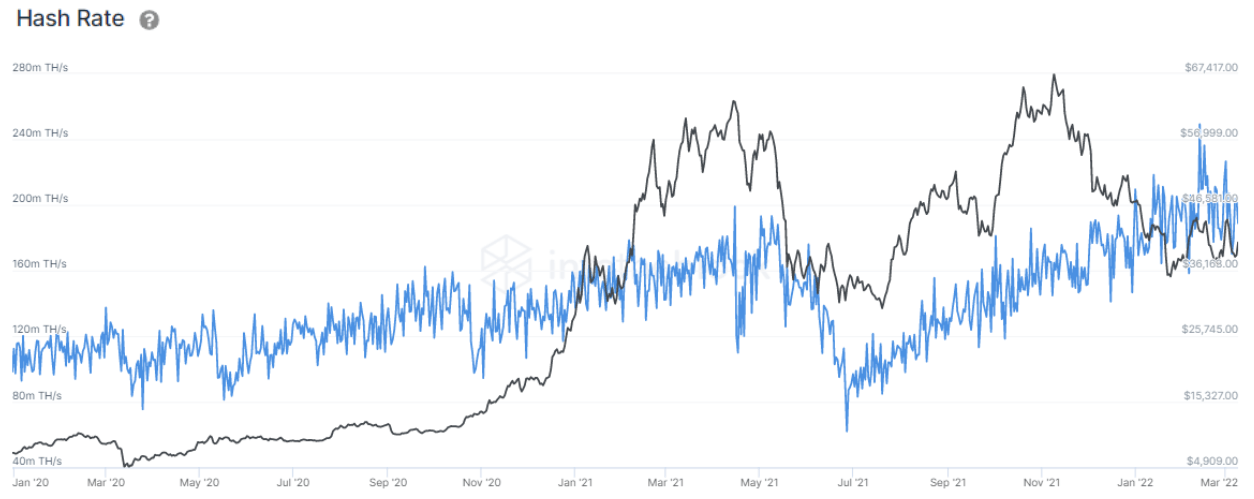
As can be seen above, Bitcoin’s hash rate has soared over the past few years, currently setting new highs at the 200m TH/s level. This is in part due to the growing industry popularity and institutions wanting to participate in the evolving market. As the hash rate increases competitiveness for mining increases as well, making the industry less profitable to existing miners.
Miner Reserves track the balance of addresses belonging to mining pools. Bitcoin miners appear to have been selling and decreasing the amount of Bitcoin in their addresses, which has dropped considerably from the beginning of 2022. Currently at the lowest since 2011, miners’ total amount of Bitcoin sits at 1.95m BTC.
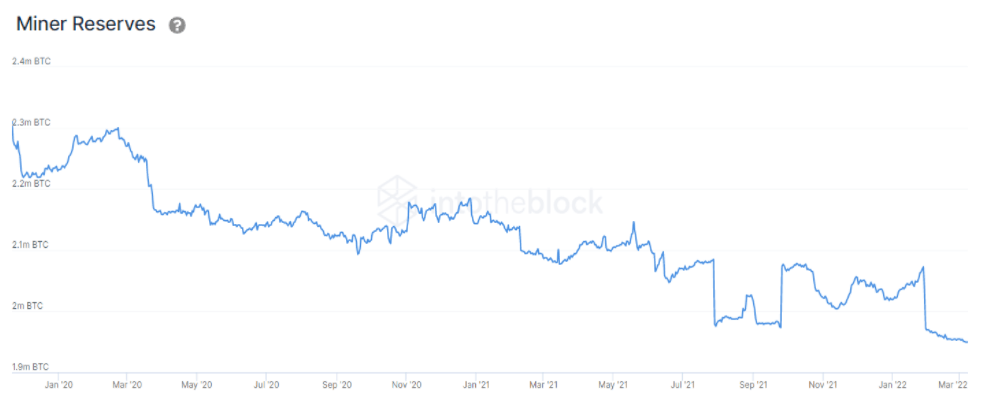
As clearly shown above Bitcoin miner reserves have decreased significantly, probably in direct relation to the Hash Rate’s robust growth. An increase in hash rate means a more competitive environment, lowering profits for miners. Similarly, Bitcoin’s decreasing price puts further pressure on miner margins.
Due to these reasons, it is likely that miners are decreasing their Bitcoin holdings in order to cover their short-term operational costs.
While miners that have held Bitcoin for years may still be able to impact Bitcoin’s price, the data shows that the marginal effect that they can have by selling has decreased significantly. The volume share pertaining to miners has constantly declined, currently sitting around 0.97% out of the total Bitcoin blockchain volume.
Asides from decreasing margins, Bitcoin mining also underwent a major change in its structure following the Chinese ban last summer. This significantly altered the distribution of mining pools and their hash rate.
Mining pools aggregate hash power between various miners to provide them higher odds of obtaining block rewards and more predictable income. IntoTheBlock measures the concentration of hash rate by mining pool.
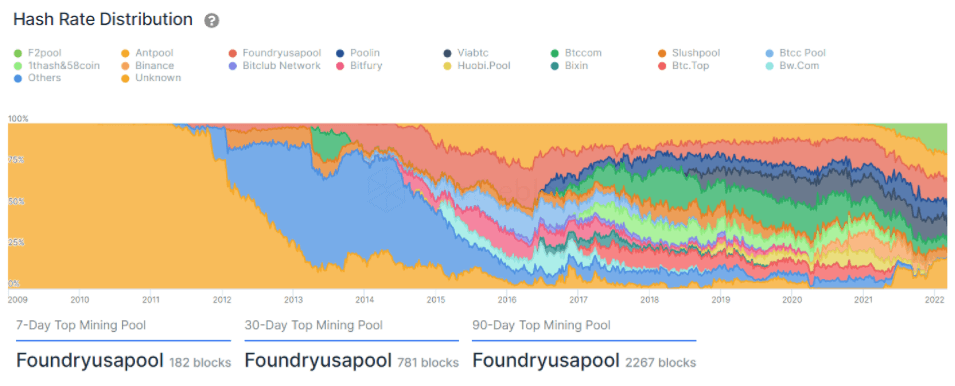
The indicator above shows mining pools hash rate distribution over time. Having passed 9 months since China’s mining crackdown, effects are being felt. Once important, Binance’s and Huobi’s Bitcoin mining pools have completely disappeared, currently, both having 0% of the total mining hash rate distribution. The fall of Bitcoin mining pools associated with China gave room for new pools to grow. In between them Foundry USA Pool, which has dominated the industry throughout the last 90 days having mined 2267 blocks.
China’s Inner Mongolia region used to be home to the majority of the digital assets mining industry. Soon after the crackdown, companies fled China and settled new permanent operations, Texas was a major beneficiary of this migration.
Subsequently, towns like Denton Texas, which after a devastating winter storm left the town in debt, have felt the positive impact. Core Scientific, a publicly-traded company, closed on a deal with the town to establish operations on their natural gas power plant and in return help secure the repayment of their loan.
In conclusion, despite miner reserves having significantly dropped throughout the years, they are not creating a significant selling pressure that could negatively affect price. The most probable cause for this decrease in holdings is their need to cover operational costs, which due to the high hash rate and low price may cause a greater impact on them. Furthermore, 9 months after the Chinese crackdown, strong ripple effects were felt throughout the mining industry.
Foundry USA Pool, a United States associated pool, has dominated the space throughout the past 90 days for their first time. Finally the United States seems to be on a road to become leaders in the mining industry with new policies being embraced.